1631. 最小体力消耗路径
大约 3 分钟
1631. 最小体力消耗路径
- 标签:深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索、并查集、数组、二分查找、矩阵、堆(优先队列)
- 难度:中等
题目链接
题目大意
描述:给定一个 大小的二维数组 ,其中 表示为位置 的高度。
现在要从左上角 位置出发,经过方格的一些点,到达右下角 位置上。其中所经过路径的花费为「这条路径上所有相邻位置的最大高度差绝对值」。
要求:计算从 位置到 的最优路径的花费。
说明:
- 最优路径:路径上「所有相邻位置最大高度差绝对值」最小的那条路径。
- 。
- 。
- 。
- 。
示例:
- 示例 1:
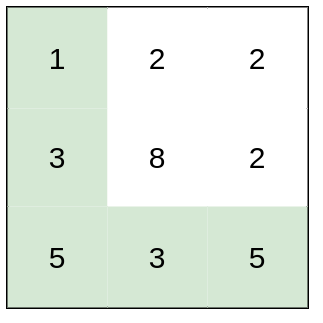
输入:heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]]
输出:2
解释:路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 连续格子的差值绝对值最大为 2 。
这条路径比路径 [1,2,2,2,5] 更优,因为另一条路径差值最大值为 3。
- 示例 2:
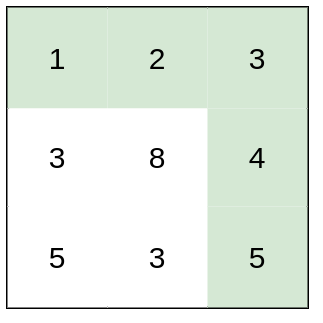
输入:heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]]
输出:1
解释:路径 [1,2,3,4,5] 的相邻格子差值绝对值最大为 1 ,比路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 更优。
解题思路
思路 1:并查集
将整个网络抽象为一个无向图,每个点与相邻的点(上下左右)之间都存在一条无向边,边的权重为两个点之间的高度差绝对值。
我们要找到左上角到右下角的最优路径,可以遍历所有的点,将所有的边存储到数组中,每条边的存储格式为 ,意思是编号 的点和编号为 的点之间的权重为 。
然后按照权重从小到大的顺序,对所有边进行排序。
再按照权重大小遍历所有边,将其依次加入并查集中。并且每次都需要判断 点和 点是否连通。
如果连通,则该边的权重即为答案。
思路 1:代码
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.parent = [i for i in range(n)]
self.count = n
def find(self, x):
while x != self.parent[x]:
self.parent[x] = self.parent[self.parent[x]]
x = self.parent[x]
return x
def union(self, x, y):
root_x = self.find(x)
root_y = self.find(y)
if root_x == root_y:
return
self.parent[root_x] = root_y
self.count -= 1
def is_connected(self, x, y):
return self.find(x) == self.find(y)
class Solution:
def minimumEffortPath(self, heights: List[List[int]]) -> int:
row_size = len(heights)
col_size = len(heights[0])
size = row_size * col_size
edges = []
for row in range(row_size):
for col in range(col_size):
if row < row_size - 1:
x = row * col_size + col
y = (row + 1) * col_size + col
h = abs(heights[row][col] - heights[row + 1][col])
edges.append([x, y, h])
if col < col_size - 1:
x = row * col_size + col
y = row * col_size + col + 1
h = abs(heights[row][col] - heights[row][col + 1])
edges.append([x, y, h])
edges.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
union_find = UnionFind(size)
for edge in edges:
x, y, h = edge[0], edge[1], edge[2]
union_find.union(x, y)
if union_find.is_connected(0, size - 1):
return h
return 0
思路 1:复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:,其中 是反 Ackerman 函数。
- 空间复杂度:。